Dive into the vibrant world of printmaking as we explore sublimation printing and screen printing. Uncover the techniques, benefits, and ideal uses for each method to guide your choice in 2025. Whether you're an artist, entrepreneur, or hobbyist, this comparison sheds light on which printing technique best suits your creative and business needs.
What Is Sublimation Printing?
Sublimation printing emerges as a dynamic method in the print on demand niche, favored for its ability to produce vibrant, full-color results.
At its core, sublimation printing involves transferring a design from special paper onto a material or object using heat and pressure. This technique allows the ink to transition from a solid to a gas without becoming liquid, embedding colors deeply into the substrate.
As a result, designs are not only durable but also resistant to fading and washing out, making it a go-to choice for custom apparel, mugs, phone cases, and more.
Unlike traditional printing methods, sublimation offers unparalleled creative freedom. Since the ink becomes part of the substrate, there's no texture or weight added to the printed item, allowing for edge-to-edge designs that maintain the original feel of the product.
How Does Sublimation Printing Work?
This printing technique involves transforming solid dye particles into gas using heat and pressure, bypassing the liquid phase. It's a process that requires specialized sublimation ink, heat press, and a substrate designed to accept the ink, such as polyester fabric or coated materials. When the ink becomes a gas, it bonds with the fibers of the substrate, resulting in a durable, high-quality print that won't crack, fade, or peel over time.
Entrepreneurs and designers find sublimation printing especially appealing for creating customized apparel, home decor, and promotional items due to its versatility and the durability of its results. Unlike traditional printing methods, sublimation allows for the creation of complex, multi-colored designs with ease.
This capability opens up a world of possibilities for businesses looking to offer detailed, custom-designed products without compromising on quality.
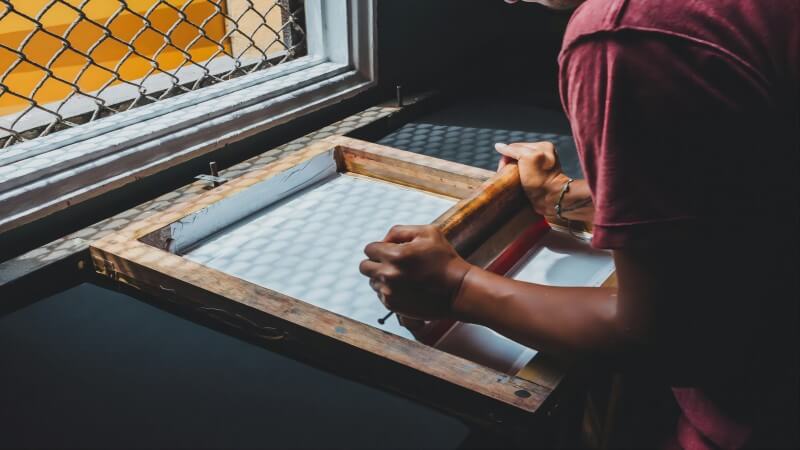

History of Sublimation Printing
Tracing the history of sublimation printing reveals a fascinating journey of innovation and creativity. This technique, which allows the transfer of designs directly onto materials, has its roots in the mid-20th century, though the concept of sublimation itself was recognized much earlier.
Initially, it found application in decorating ceramics and hard substrates, but as technology evolved, so did the versatility of sublimation printing. Advances in digital printing technology in the late 20th century significantly broadened its scope, enabling its use on a wide range of textiles and other materials.
Designers, artists, and businesses today leverage this method to produce everything from vibrant apparel and signage to personalized home decor. Its ability to render intricate, full-color images with precision has made it a favored choice among those looking to push the boundaries of custom merchandise.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sublimation Printing
Sublimation printing offers a world of advantages for those looking to produce vibrant, full-color designs on a variety of substrates. One of the most notable benefits is the quality of the print; sublimation ink bonds directly with the material, resulting in high-definition, photorealistic images that are resistant to fading and cracking.
Additionally, sublimation printing is highly versatile, suitable for small batch runs, which makes it ideal for entrepreneurs and designers who wish to experiment with different designs without committing to large inventory volumes.
However, sublimation printing is not without its drawbacks. The process requires a significant upfront investment in specialized equipment, including a sublimation printer, heat press, and substrates that are compatible with sublimation ink. Moreover, it's limited to materials that are either polyester-based or have a special polymer coating, which can restrict the range of products you're able to offer.
Despite these challenges, the unique benefits of sublimation printing continue to make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications, offering unmatched durability and design flexibility.
What Is Screen Printing?
Screen printing is a time-honored technique used for transferring ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil.
The technique is favored for its versatility, allowing for printing on various materials such as textiles, ceramics, wood, paper, glass, and metal.
A distinct advantage of screen printing is its exceptional vibrancy for prints that are exposed to the outdoors or subjected to significant wear and tear. This durability comes from the composition and thickness of the ink used in the process, which is especially relevant for apparel and signage in demanding environments.
However, it's important to note that screen printing is most cost-effective for larger batches due to the setup required for each stencil. While it offers less detail than digital printing methods like sublimation, its ability to produce rich, solid colors makes it a popular choice for high-impact graphics and bold designs. Entrepreneurs, artists, and designers often gravitate towards screen printing when they're looking to execute large orders of merchandise with a few colors, benefiting from its scale of economy and lasting quality.
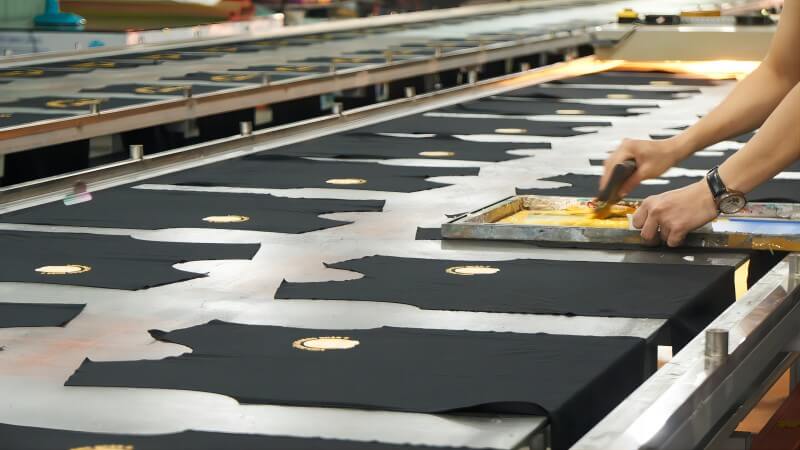

How Does Screen Printing Work?
Screen printing operates on a straightforward yet versatile principle, making it a popular choice for printing on various materials. The process begins with creating a stencil, also known as a screen, which is used to apply layers of ink on the printing surface.
Then a blade or squeegee is moved across the screen stencil, forcing ink through the mesh openings to imprint the design onto the substrate below.
This technique shines in its ability to produce vibrant, long-lasting colors and is highly adaptable for large-scale production runs. Screen printing ink is thicker than what's used in other methods, resulting in richer, more dynamic colors that stand up well to washing and heavy use. Ideal for textiles, posters, and a wide array of promotional items, screen printing has cemented its role in the print industry due to its durability and efficiency.
History of Screen Printing
Screen printing's roots stretch back over a millennium, making it one of the oldest printing techniques known to man. Originating in China during the Song Dynasty, it began as a method of using silk screens to apply ink to fabrics. This ancient craft was refined over centuries, spreading through Asia and eventually reaching Western Europe in the late 18th century.
However, it wasn't until silk mesh became more accessible in the 19th century that screen printing began to gain popularity in the artistic and commercial fields in the West.
The evolution of screen printing over the 20th century marked its transformation into a key tool for both artistic expression and commercial application. Innovations in photo-reactive chemicals allowed for the development of photo-imaging stencils, revolutionizing the process and enabling more detailed and intricate designs.
Screen printing's rich history and adaptability ensure its continued relevance in both artistic and commercial spheres today.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Screen Printing
Screen printing, a method revered for its versatility and history, stands out for its capacity to produce vibrant, long-lasting designs on a wide array of materials. This technique, which involves pushing ink through a mesh screen onto the substrate, allows for the creation of durable, high-quality prints.
Its principal advantage is the vibrancy and opacity of colors it can achieve, particularly on darker fabrics, making it a favorite for textile applications. Screen printing's ability to handle large volumes efficiently also makes it economically viable for businesses planning extensive production runs.
However, screen printing does come with its set of challenges. The initial setup for screen printing can be time-consuming and costly, particularly for designs that require multiple colors. Each color needs its screen, increasing the complexity and production time. This setup makes it less ideal for small orders or designs that frequently change.
Additionally, the intricacy of designs can be somewhat limited compared to digital methods like sublimation printing, as each color needs to be applied separately. Despite these drawbacks, screen printing's durability, cost-effectiveness for large batches, and color vibrancy maintain its popularity among businesses and designers alike.

Sublimation vs. Screen Printing: Main Differences
When comparing sublimation and screen printing, the main distinctions lie in their processes, output, and suitability for different projects. Each method offers unique advantages, making them preferable under various circumstances.
Process and Technique
Sublimation printing is a digital printing method that uses heat-sensitive inks to transfer images onto synthetic materials. It's known for its ability to produce vibrant, full-color images with high detail.
This technique involves the ink turning into gas under heat and pressure, which then bonds with the fabric or material, resulting in a durable and fade-resistant print. It's particularly effective for polyester fabrics and coated items, making it ideal for custom apparel, promotional products, and decorative items.
Screen printing, on the other hand, is a more traditional method involving the transfer of ink onto a substrate through a mesh screen. It requires creating a stencil (or screen) for each color layer of the design, making it best suited for designs with fewer colors.
This method is celebrated for its versatility across materials, including textiles, ceramics, wood, and paper, offering a high degree of vibrancy and durability, especially on cotton and cotton blend fabrics.
Output Quality and Durability
Sublimation shines when it comes to intricate designs and color gradients, as it allows for a seamless integration of the print with the material. The end product is less prone to fading or cracking over time, given that the ink is embedded within the substrate rather than sitting on top.
However, its limitation to light-colored, synthetic materials can be a drawback for projects requiring natural fibers or darker materials.
Screen printing is renowned for its durability and the tactile quality it lends to prints, with ink layers sitting atop the material's surface, offering a distinct texture. While it can produce vivid, opaque prints on a variety of materials and fabric colors, the method can be less cost-effective and more labor-intensive for multi-colored designs, particularly for smaller batches.
While sublimation offers unparalleled detail and durability for synthetic materials, screen printing remains a go-to for high-volume, durable prints across a broad range of materials.
Sublimation vs. Screen Printing: Which One Is Best for Your Business?
Deciding between sublimation and screen printing for your business pivots on understanding your product range, customer preferences, and design intricacies. Sublimation printing, distinguished by its digital precision,this method excels when producing items with complex color patterns or gradients, offering a no-feel print that becomes part of the item itself. It's especially suitable for businesses focusing on custom apparel, accessories, and home decor that demand high-quality imagery and durability in their products.
Conversely, screen printing has its roots in versatility and tradition, being able to accommodate a broader spectrum of materials including cotton, canvas, and even metal. Screen printing may be more cost-effective for larger orders with fewer colors, but it requires a more substantial setup, which might not be ideal for businesses looking for flexibility and low upfront costs.

Final Thoughts
Wrapping up the discussion on sublimation versus screen printing, it's clear both techniques offer unique benefits tailored to different business needs and creative visions.
Ultimately, the decision between sublimation and screen printing boils down to your business model, product types, and the expectations of your target audience. By carefully considering these factors, you can select a printing method that not only enhances your product offerings but also aligns with your brand values and market demands.
Remember, the choice of printing technique is a crucial component of your product development process, one that can significantly impact the perceived value and appeal of your merchandise in a competitive market.
FAQs
Which is cheaper screen printing or sublimation?
Screen printing often comes out cheaper for larger orders with fewer colors, while sublimation can be cost-effective for smaller, more detailed designs.
Are there dangers from a sublimation print?
Sublimation printing is generally considered safe, with minimal dangers when proper ventilation and safety practices are followed.
Does sublimation last as long as screen printing?
Sublimation can last equally long, if not longer than screen printing, depending on the substrate and usage.
Is sublimation printing waterproof?
Yes, sublimation prints are waterproof as the dye bonds with the material on a molecular level.
Is sublimation better than silk screen?
Sublimation and silk screen each have unique benefits; the best choice depends on project specifics.








 Global Shipping
Global Shipping








 Made in USA
Made in USA