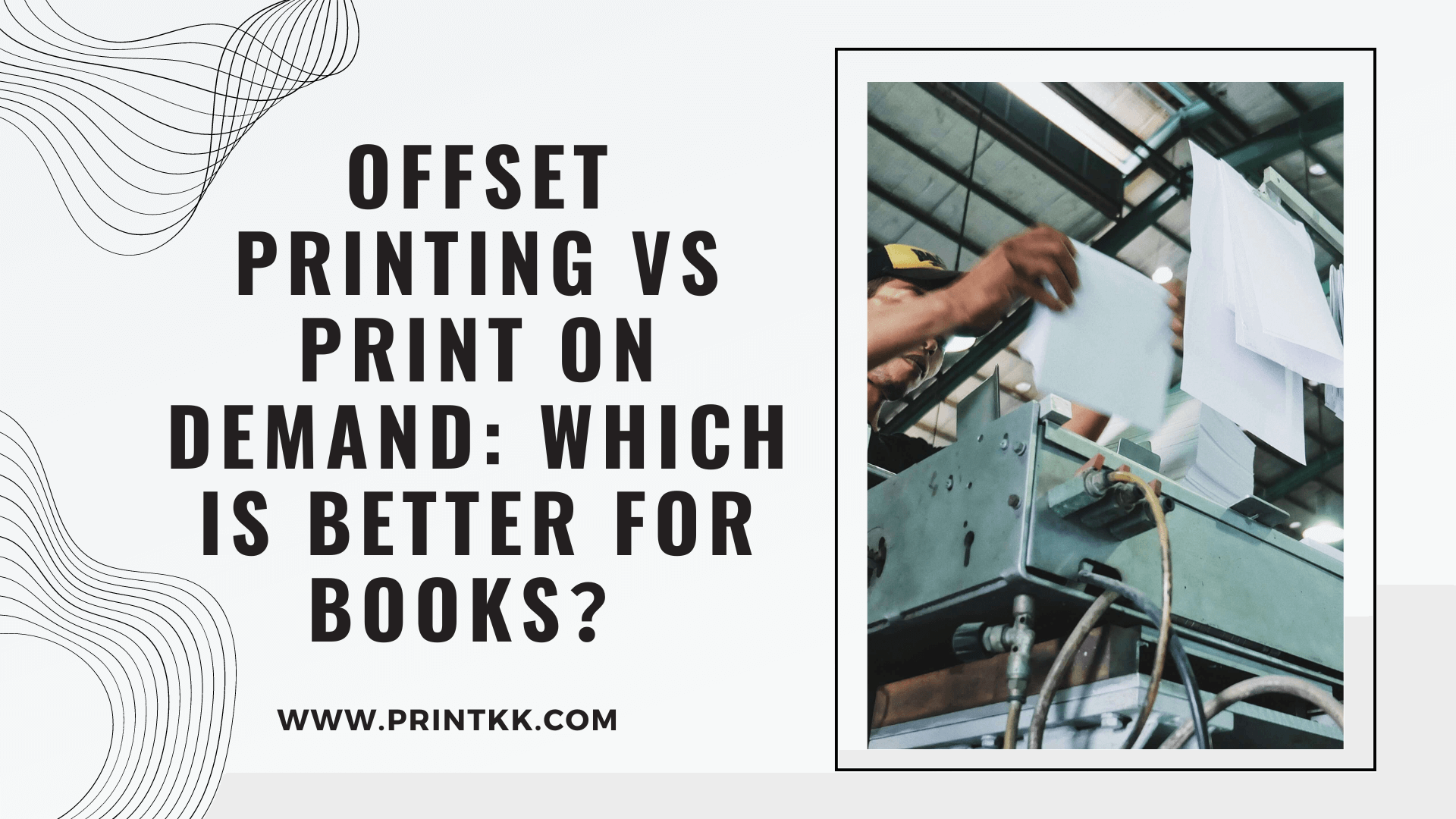
Selecting the appropriate printing method can revolutionize your book publishing experience. Dive into the dynamic world of offset printing and print on demand, where we explore the efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of each option. Get ready to make an informed decision that brings your book to life in the best possible way, ensuring it reaches your audience with the impact it deserves.
What Is Offset Printing?
Offset printing is a conventional printing technique where images are transferred from a plate to a rubber blanket, and then onto the printing surface. This method is renowned for delivering high-quality, consistent prints with vivid colors and precise details. Offset printing is commonly used for books, newspapers, magazines, and marketing materials, where superior quality and uniformity are paramount.
This technique requires the creation of a metal plate for each color in the print job, which can be both time-consuming and expensive for small runs. However, offset printing accommodates a wide variety of paper types and finishes, providing flexibility in the final product's appearance and texture. Its ability to produce rich, detailed images makes it a preferred choice for projects that demand the highest print quality.
How Is the Cost of Offset Printing Calculated?
The initial set-up costs for offset printing are high, including plate making and press calibration. The unit cost decreases as the print volume increases, making it cost-effective for large-scale print runs. Factors like paper quality, ink type, and finishing options (e.g., coatings or bindings) also influence the total cost.
The costs of labor, maintenance and energy consumption also need to be considered. This makes offset printing ideal for high-volume projects where the setup costs are offset by the lower per-unit cost as production scales up.
The Pros and Cons of Offset Printing
Pros
High Image Quality:
Offset printing is renowned for its exceptional image quality. This process uses high-resolution printing plates that produce sharp and consistent images. The detail and color accuracy achieved through offset printing make it ideal for high-end publications, marketing materials, and products where visual impact is critical.
Cost-Effective for Large Runs:
A major benefit of offset printing is its cost-efficiency for large print runs. While the initial setup costs can be steep because of the need to create printing plates, the cost per unit drops significantly as the quantity increases. This makes it a budget-friendly option for bulk orders, including newspapers, books, and extensive marketing campaigns.
Versatility in Printing Surfaces:
Offset printing can be utilized on a range of surfaces beyond paper, such as cardboard, plastic, and metal. This versatility allows businesses to use offset printing for a wide range of products, from packaging and labels to promotional materials, expanding its application beyond standard paper products.
Faster Production for High Volume:
Once set up, offset printing machines can run at high speeds, producing large quantities of prints in a relatively short amount of time. This efficiency makes it a preferred choice for projects with tight deadlines and high volume requirements, ensuring timely delivery without compromising quality.
Color Consistency:
Offset printing ensures superb color consistency throughout the entire print run. The use of Pantone inks and precise color mixing ensures that each copy matches the intended design, which is crucial for brand consistency and professional appearance.
Cons
High Initial Setup Costs:
The primary drawback of offset printing is the high initial setup costs. Creating the printing plates and configuring the press can be expensive, making offset printing less cost-effective for small print runs. These setup costs need to be amortized over a large number of copies to make the process economical.
Longer Turnaround Time for Setup:
The setup process for offset printing is more elaborate and time-intensive than that of digital printing. This includes the preparation of plates, alignment, and calibration of the press. As a result, the initial turnaround time can be longer, which might not be suitable for projects requiring immediate printing.
Limited Cost Efficiency for Short Runs:
Due to the high setup costs, offset printing is not cost-efficient for small quantities. Digital printing, with its lower initial costs and flexibility, is often a better choice for short print runs. Offset printing becomes economically viable only when the volume justifies the setup expense.
Environmental Impact:
Offset printing involves the use of chemicals and inks that can have an environmental impact. The process generates waste materials such as plates and chemical solvents. While advancements have been made to reduce this impact, offset printing is generally considered less environmentally friendly than digital alternatives.
Complexity in Changes:
Making changes to the design or text in offset printing can be cumbersome and expensive. Any modification necessitates the creation of new plates, which increases both the cost and the time required. This inflexibility makes it less suitable for projects that might require frequent updates or adjustments during the printing process..jpg)
What Is Print on Demand?
Print on Demand (POD) for books is a revolutionary approach to publishing that allows authors and publishers to print copies only when an order is placed. This method does away with the need for large print runs, thereby minimizing the risk of unsold inventory and high initial costs. With POD, authors can bring their work to market quickly and efficiently, making it an ideal solution for self-publishers, small presses, and niche authors.
In the print on demand process, the manuscript is uploaded to a POD platform, where it can be formatted and customized. When a customer orders a book, the platform prints a single copy or the required number of copies, ensuring that each book is printed, bound, and shipped directly to the buyer. This technology allows for high-quality printing, with options for various formats, sizes, and cover types, providing flexibility and professional results.
How Is the Cost of Print on Demand Calculated?
The cost of print on demand (POD) is determined by several factors. The base cost per unit includes raw materials like paper and ink, and remains consistent regardless of order size. Production costs also depend on design complexity, number of colors, and binding or finishing types.
Unlike offset printing, POD maintains a consistent price per unit, making it ideal for small quantities without high upfront costs. Setup fees are usually minimal, further benefiting those with limited print runs. This makes POD a flexible and cost-effective option for various printing needs.
The Pros and Cons of Print on Demand
Pros
Lower Initial Investment:
Print on demand (POD) requires a significantly lower upfront investment compared to offset printing. There's no need to print large quantities to justify the cost, which makes it an attractive option for small businesses and individual creators. With POD, you only pay for what you require, which reduces financial risk and minimizes unsold inventory.
Flexibility and Customization:
POD offers unmatched flexibility and customization options. You can easily update designs, change products, or test new ideas without incurring substantial costs. This flexibility enables the creation of personalized products, catering to specific customer preferences and trends. It's particularly beneficial for artists and designers looking to offer unique, one-of-a-kind items..jpg)
Reduced Storage and Waste:
With POD, items are printed on demand, eliminating the need for extensive storage space and reducing waste. This just-in-time production model is environmentally friendly and cost-effective, as it prevents overproduction and the associated costs of storing unsold goods. It also facilitates straightforward inventory management.
Scalability:
POD enables effortless scalability. Regardless of whether you receive a single order or a thousand, the process stays streamlined and efficient. This is ideal for businesses experiencing fluctuating demand or seasonal sales peaks, as you can scale production up or down without worrying about overstocking or underproduction.
Easy Entry to Market:
POD reduces the entry barriers for new businesses. Entrepreneurs and creators can begin selling products online without requiring substantial capital investment. This democratizes the market, allowing more people to launch their own brands and test their ideas with minimal risk.
Cons
Limited Control Over Quality:
Since POD often involves third-party services, you might have less control over the production process. This can result in inconsistencies in print quality, color accuracy, and material standards. It's essential to choose reliable POD providers to ensure your products meet your quality expectations and customer satisfaction.
Dependence on Supplier Reliability:
Your business relies significantly on the dependability and efficiency of your POD supplier. Any disruptions in their operations, such as technical issues or delays, can directly impact your ability to fulfill orders on time. Establishing a robust relationship with a reliable supplier is essential for ensuring seamless operations.
Limited Product Range:
POD services may offer a limited range of products compared to traditional printing methods. This might limit your capacity to diversify your product range or venture into new categories. It's important to research and choose a POD provider that offers a wide selection of products to meet your business needs.
Offset Printing vs Print on Demand: Which Is Better for Books?
When deciding between offset printing and print on demand (POD) for books, weigh the benefits of each. Offset printing is economical for large print runs, with per-unit costs diminishing as the quantity rises. Offset printing also offers superior print quality and a wider range of paper types and finishes, which can enhance the book's overall appeal and durability.
Print on demand is perfect for small print runs and self-publishers due to its flexibility and lower initial investment. Books are printed on demand as orders are received, which lowers upfront expenses and minimizes waste. POD allows for easy updates and revisions to the book, which can be beneficial for authors who wish to make frequent changes.
The decision between offset printing and print on demand largely hinges on your particular requirements. For large quantities and high-quality finishes, opt for offset printing. For flexibility, lower costs, and minimal waste, print on demand is ideal. Each method has its own advantages, and understanding these can assist you in making an informed choice for your book printing requirements..jpg)
The Best Way to Print Books at Home
Printing books at home can be a cost-effective and flexible option for authors and small publishers. This approach enables you to print books as orders are received, thereby eliminating the necessity for large print runs and reducing storage expenses.
Print-on-demand technology enables you to rapidly design and prototype new book formats, from novels to custom planners, allowing you to respond quickly to market trends and customer preferences. This capability ensures your books remain relevant and appealing to readers seeking personalized content.
With print-on-demand, you can focus more on writing and marketing your books while relying on a robust fulfillment system to efficiently satisfy customer orders. Using print-on-demand for your home book printing needs ensures high-quality results and a streamlined process.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate printing method depends on your unique requirements, budget, and objectives. By comprehending the strengths and limitations of each option, you can make a well-informed decision that best aligns with your project. Whether you opt for the traditional reliability of offset printing or the modern convenience of print on demand, both options provide viable pathways to bringing your printed materials to life.
FAQs
What are the common ways of printing books?
Common ways of printing books include offset printing, print on demand, letterpress printing and gravure printing.
What is the most expensive printing method?
For books, the most expensive printing method is usually letterpress printing. This traditional technique involves manually setting type and pressing paper onto inked plates, which is labor-intensive and time-consuming.
What is the difference between printing on demand and direct delivery?
Print on demand entails manufacturing items solely when an order is placed. Direct delivery refers to shipping products directly from the manufacturer to the customer, often used in dropshipping models.
How long will it take to offset printing?
For small runs, it may take several days, while larger orders can take weeks, depending on the complexity and volume of the print job.








 Global Shipping
Global Shipping